WHAT IS MICROFERTILIZER? – WHY MIGURE FERTILIZER HAS TO BE FERTILIZED?
For plants to grow well, they need to be provided with enough macro, medium and micronutrients. Although some micronutrients are needed in very small amounts, they are sometimes very important for plants. The lack or excess of micronutrients also greatly affects plants. Therefore, fertilizing with micronutrients is extremely necessary
What are micronutrients?
Micronutrients are a mixture of chemicals that provide trace elements for plants. Sometimes, they also add super trace elements, rare earths, and growth stimulants.
Excess micronutrients can cause plants to be stunted, slow to grow, or contaminated with heavy metals, affecting the quality of agricultural products and human health. Some micronutrients also create the characteristic flavors of that plant.

What is micronutrient fertilizer?
Why do we need to fertilize with micronutrients?
Micronutrient fertilizer is an extremely necessary fertilizer for plants
- It participates in the structure of living matter
- Regulates metabolism and physiological activities in plants.
- Changes the physical and chemical properties of protoplasm.
- Activates enzymes, increases metabolism.
- Regulates plant growth.
- Increases plant resistance.
From the above advantages, micronutrient fertilizers have become an indispensable fertilizer for plants.
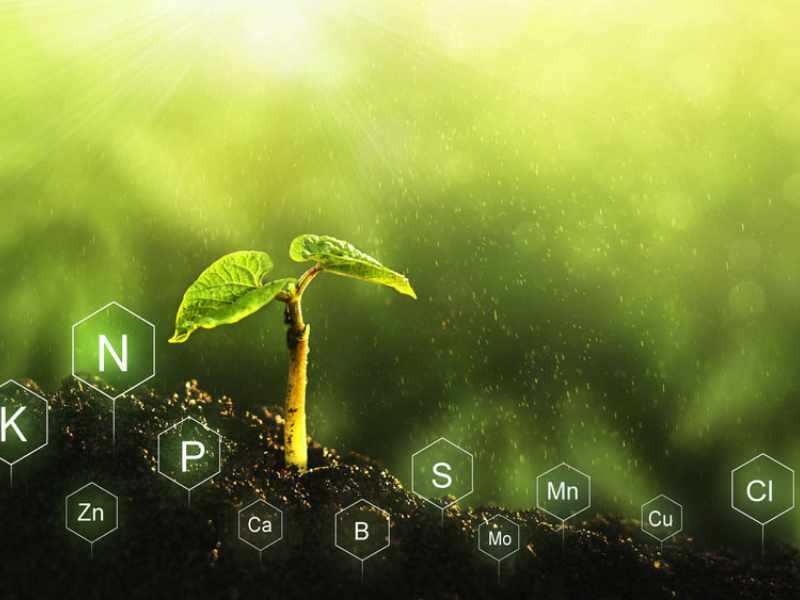

Why do we need to fertilize with micronutrients?
The role of essential micronutrients for plants
1. Copper (Cu)
Role:
- Necessary in the formation of chlorophyll and catalyzing other reactions in plants, but usually does not participate in their components.
- Promotes the formation of vitamin A.
- Increases the absorption efficiency of other trace elements such as Zinc, Manganese, Boron, etc.
Cause:
- Copper deficiency often occurs in sandy soils, peat soils, soils with high organic content, and newly reclaimed land and acidic soils.
- Plants lacking copper often have gummosis (very common in fruit trees), accompanied by necrotic spots on leaves or fruits.

Copper trace element
2. Iron trace element (Fe)
Role:
- Is a trace element necessary for the growth and development of plants, promoting the activities of many enzymes that directly affect the biochemical processes in plants
- Forming chlorophyll, making leaves green, playing an important role in the photosynthesis process of plants.
- Forming organic molecular compounds, helping the protein synthesis process
Cause:
- Iron is not reused, so iron deficiency is likely to occur when fertilizing is unbalanced, causing an imbalance in Cu, Mn, Mo, and a lot of CO2
- Soil with high pH (due to liming, low humidity, high phosphate fertilizer), high carbonate content
- Due to plant genetics
- Due to low organic matter content in the soil
- Iron deficiency occurs on alkaline soil, acidic soil, soil with high phosphorus content.
Use manure and green manure to supplement iron for the soil or apply micronutrient fertilizers to supplement iron for plants.

Trace element Iron (Fe)
3. Trace element Manganese (Mn)
Role:
– Makes roots big, germinates early, flowers evenly, has high fruit set rate, and firm seeds.
– Contributes to creating enzymes, activating some important metabolic reactions in plants: nutrient absorption, nitrogen fixation, nitrate reduction.
– Participates directly in the process of photosynthesis, respiration, organic matter synthesis, transport, water vapor metabolism, glucid metabolism, growth and development (germination, stem formation and flowering and fruiting), drought resistance of plants.
Cause:
– Manganese deficiency often occurs in alkaline soils, acidic soils after liming, well-ventilated soils and organic-rich soils
– Imbalance with other nutrients such as Calcium, Magnesium and Iron is also the cause of Manganese deficiency.
– Cold weather conditions and waterlogging also cause Mn deficiency
Use manganese sulfate fertilizer (MnSO4.5H2O) to treat seeds, spray on leaves, and apply to soil to supplement manganese for plants.

Trace element Manganese (Mn)
4. Trace element Zinc (Zn)
Role:
– Zn participates in activating about 70 enzymes of many physiological and biochemical activities of plants. Zinc deficiency causes a significant reduction in plant productivity.
– Zinc supports the synthesis of growth substances and enzyme systems and is necessary for enhancing some metabolic reactions in plants. It is necessary for the production of Chlorophyll and Hydratcarbons.
– Increases drought tolerance and the ability to use phosphorus and nitrogen.
Causes:
– Unbalanced fertilization.
Use zinc sulfate (ZnSO4.7H2O) to treat seeds or spray on leaves at a concentration of 0.02-0.05% or use other zinc-containing fertilizers to supplement zinc for plants.

Trace element Zinc (Zn)
5. Trace element Boron (B)
Role:
- Boron is necessary for pollen germination, pollen tube growth, cell wall and seed formation.
- Boron directly affects cell differentiation, hormone exchange, N, water and other mineral exchange.
- Boron helps increase the plant's resistance to lodging because it increases protein synthesis (avoids NH3 toxicity) and glucid synthesis
- Boron is beneficial for flowering and fruit formation, increases the transport of substances to help plants grow and increase drought resistance
Cause:
- Unbalanced fertilization, fertilizers do not contain enough necessary micronutrients leading to micronutrient deficiency.
Supplement B for plants by applying B-containing fertilizers such as NPK+ TE, Borax, and other synthetic micronutrient fertilizers.
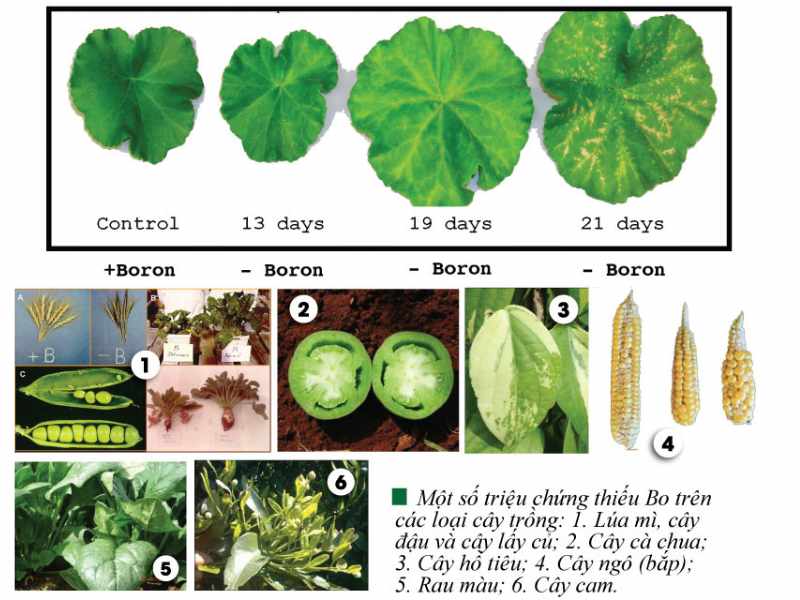

Micronutrient Boron (B)
6. Micronutrient Molybdenum (Mo)
Role:
– Necessary for the synthesis and activity of nitrate reductase.
– Promotes the process of consolidating and using nitrogen in plants.
– Necessary for symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in nodules on legumes.
– Necessary for the conversion of phosphorus from inorganic to organic in plants.
Cause:
– Mo deficiency often occurs in acidic soils.
– Light soils are more susceptible to Mo deficiency than heavy soils.
Mo can be supplemented with organic fertilizers to supplement plants.

Trace element Molybdenum (Mo)
7. Trace element Chlorine (Cl)
Role:
– Chlorine is a vital trace element for plants.
– Participates in energy conversion reactions in plants.
– Activates enzymes.
– Transports calcium, magnesium, potassium in plants.
– Controls plant water vapor.

Trace element Chlorine (Cl)
Signs of micronutrient deficiency in plants
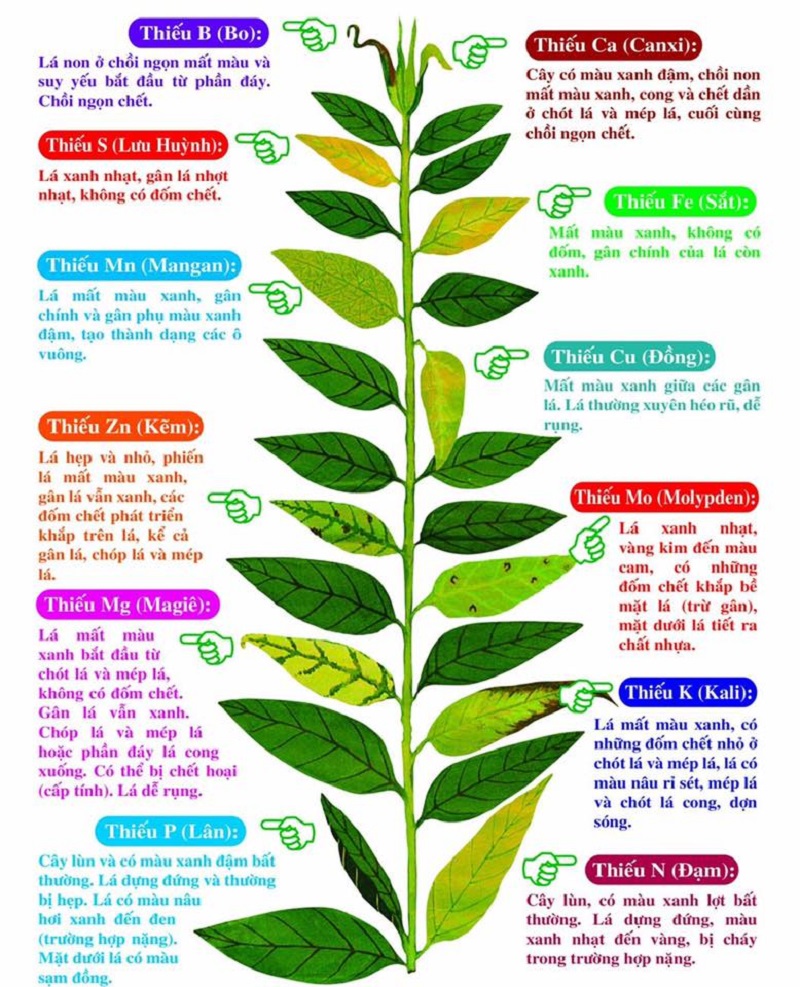
Signs of micronutrient deficiency in plants
For plants, micronutrients are extremely important. They determine the productivity of plants. The lack or excess of micronutrients greatly affects plants. We need to pay attention to plants to be able to provide enough micronutrients for plants.
Our company VNT specializes in providing micronutrient fertilizers. The leading prestigious quality in Vietnam. We always put the interests of customers first. Contact to order as soon as possible to receive many incentives from the company







![[Q&A] How Long After Applying NPK Fertilizer Can You Eat Vegetables?](https://vntradimex.com/public/files/news/bon-phan-npk-cho-rau-bao-lau-thi-an-duoc-685e204cde416.jpg)

![[SHARE] How to use NPK fertilizer properly that everyone should know!](https://vntradimex.com/public/files/news/cach-dung-phan-bon-npk-dung-cach-682c46ab907d2.jpg)




