Ethanol – C2H5OH – Applications and unpredictable harms
Ethanol is a compound that is very familiar to most people. It has many practical applications that serve human life. Want to learn more about this compound? Let’s explore ethanol with VNT.
What is Ethanol? Understanding the Ethanol Compound
Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol or ethanol alcohol, is an organic compound widely used in daily life. Its chemical formula is C₂H₆O or C₂H₅OH.
Physical Properties of Ethanol:
- It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic smell, volatile, and easily soluble in water and many other organic substances.
- When burned, ethanol produces a blue flame along with CO₂ and water vapor.
- In its pure form, ethanol has hygroscopic properties (absorbs moisture from the air).
- Ethanol melts at -117.3°C and boils at 78.5°C.
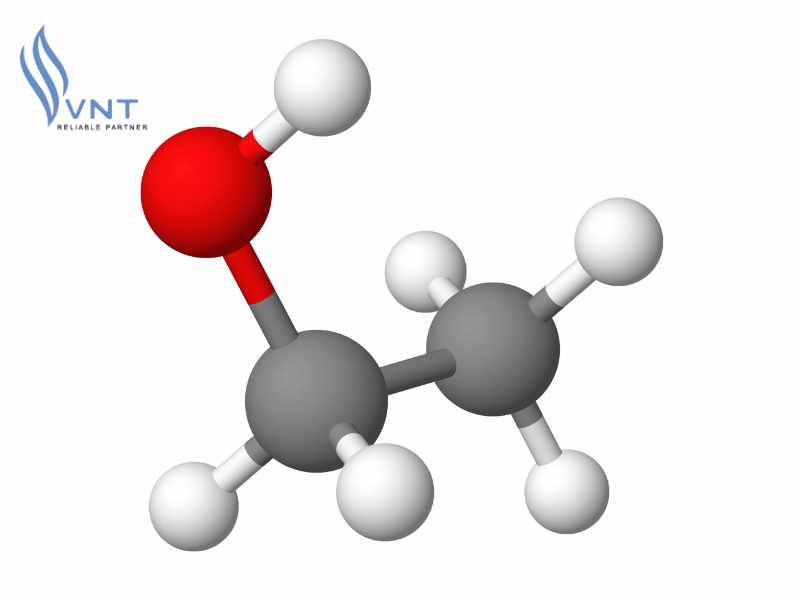
The chemical formula of ethanol is C₂H₅OH
Applications of Ethanol in Real Life
Ethanol has many uses in daily life and is favored by many people:
- Ethanol is used to blend with biofuel, often making up more than 90% of the mixture.
- It is used in the chemical industry as a solvent for perfumes and cosmetics.
- Applied in the industrial cleaning sector for disinfection and cleaning.
- Used in beverage production, such as alcoholic drinks, and in the food industry for flavoring and marinating.
- In the printing industry, ethanol also sees extensive application.
- In healthcare and pharmaceuticals, ethanol is used as a disinfectant and a solvent for drug preparation.
- Ethanol is used in cosmetics, such as nail polish, and in antifreeze products.
- Additionally, it is used for cleaning microcircuits in the electronics industry.
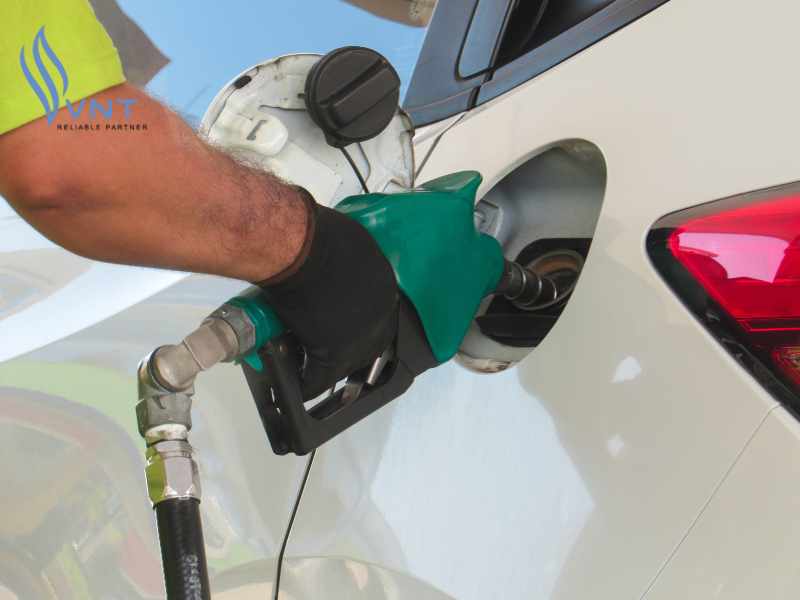

Applications of Ethanol in Real Life
The Dangers of Ethanol
Despite its undeniable benefits, ethanol also poses serious risks. Here are some potential dangers associated with ethanol:
- Ethanol is highly flammable and easily ignited, posing fire and explosion hazards if not stored properly.
- When inside the human body, ethanol is metabolized into acetaldehyde – a highly toxic compound linked to diseases such as liver cirrhosis and cancer.
- Blood ethanol concentrations of 0.4–0.5% or higher can be fatal. Concentrations of 0.3–0.4% may cause coma.
- Ethanol has a direct correlation with the growth of Acinetobacter baumannii, a bacterium that causes pneumonia, meningitis, and urinary tract infections.

The Dangers of Ethanol
Precautions When Storing Ethanol
Ethanol is a compound with many useful applications. To maintain its quality and ensure user safety, consider the following precautions:
- Ethanol should be stored in specialized containers with clear labeling, kept in a dry, well-ventilated place, and out of children’s reach.
- When used industrially, protective clothing must be worn to prevent burns.
- Containers should not be filled more than two-thirds full to prevent ethanol expansion.
- Pure ethanol must not be diluted and consumed unless dosage is clearly known.
- In case of ethanol fires, use dry chemicals or CO₂ to extinguish. Do not use water, as it can spread the fire due to ethanol's solubility.
These are VNT’s insights into ethanol. In everyday life, ethanol is an extremely common and useful resource for every household.







![[Q&A] How Long After Applying NPK Fertilizer Can You Eat Vegetables?](https://vntradimex.com/public/files/news/bon-phan-npk-cho-rau-bao-lau-thi-an-duoc-685e204cde416.jpg)

![[SHARE] How to use NPK fertilizer properly that everyone should know!](https://vntradimex.com/public/files/news/cach-dung-phan-bon-npk-dung-cach-682c46ab907d2.jpg)




